Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Fukuda, Kodai; Yamane, Yuichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(12), p.1514 - 1525, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study aims to clarify the effect of fuel particle radius on the criticality transient behavior and the total number of fissions in water-moderated solid fuel dispersion systems. Neutronics/thermal hydraulics-coupled kinetics analysis was performed in a hypothetical fuel debris system, where small fuel particles aggregate in water and become supercritical. Results showed that the number of fissions is 10 times larger when the fuel particle radius is reduced by one order of magnitude under conditions where heat transfer, i.e. from fuel to water, is emphasized. Moreover, there is a possibility that lower reactivity could give a larger number of fissions when the fuel particle size is very small. In addition, the number of fissions may be overestimated or underestimated to an unexpected extent unless appropriate fuel particle size is set on the analysis.
Fukuda, Kodai
Proceedings of 4th Reactor Physics Asia Conference (RPHA2023) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2023/10
Brief evaluations were performed using the N-F model to quantitatively clarify the effect of thermal expansion on the consequences of criticality accidents in the water-moderated fuel-particle-dispersion system. The analysis clarified that ignoring thermal expansion can lead to underestimation or overestimation of the consequences by several tens of percent. It is concluded that evaluators can ignore the thermal expansion when they evaluate the consequences of the prompt supercritical transient in water-moderated solid fuel-dispersion systems, such as fuel debris systems. Only the Doppler effect can be considered when the fuel-temperature-feedback coefficient is prepared. However, depending on the required accuracy, the evaluators should take care of the error caused by ignoring thermal expansion.
Togawa, Orihiko; Okura, Takehisa; Kimura, Masanori
JAEA-Review 2022-049, 76 Pages, 2023/01
Before construction and after operation of nuclear facilities, environmental consequence assessments are conducted for normal operation and an emergency. These assessments mainly aim at confirming safety for the public around the facilities and producing relief for them. Environmental consequence assessments are carried out using observations/ measurements by environmental monitoring and/or model predictions by calculation models, sometimes using either of which and at other times using both them, according to the situations and necessities. First, this report investigates methods, roles, merits/demerits and relationship between observations/measurements and model predictions which are used for environmental consequence assessments of nuclear facilities, especially holding up a spent nuclear fuel reprocessing plant at Rokkasho, Aomori as an example. Next, it explains representative examples of utilization of data on observations/measurements and results on model predictions, and considers points of attention at using them. Finally, the report describes future direction, for example, improvements of observations/measurements and model predictions, and fusion of both them.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2022-043, 52 Pages, 2023/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Fuel debris criticality analysis technology using non-contact measurement method" conducted in FY2021. The purpose of research was to improve the fuel debris criticality analysis technology using non-contact measurement method by the development of the fuel debris criticality characteristics measurement system and the multi-region integral kinetic analysis code. It was performed by Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), and National Research Nuclear University (MEPhI) as the first year of four years research project. For the criticality characteristic measurement systems to be developed by the Japanese and Russian sides, …
Ishida, Shinya; Fukano, Yoshitaka; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Okano, Yasushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 13 Pages, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Yamane, Yuichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(11), p.1331 - 1344, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The reactivity was estimated from a time profile of neutron count rate or a simulated data in a quasi-steady state after sudden change of reactivity or external neutron source strength. The estimation was based on the equation of power in subcritical quasi-steady state. The purpose of the study is to develop the method of timely reactivity estimation from complicated time profile of neutron count rate. The developed method was applied to the data simulating neutron count rate created by using one-point kinetics code, AGNES, and Poisson-distributed random noise and to the transient subcritical experiment data measured by using TRACY. The result shows that the difference of the estimated and reference value was within about 5% or less for (
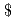
 -1) for simulated data and within about 7% or less for
-1) for simulated data and within about 7% or less for 
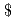
 -1.4 and -3.1 for the experimental data. It was also shown that the possibility of the reactivity estimation several ten seconds after the status change.
-1.4 and -3.1 for the experimental data. It was also shown that the possibility of the reactivity estimation several ten seconds after the status change.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2021-037, 61 Pages, 2022/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Improvement of critical safety technology in fuel debris retrieval" conducted in FY2019 and FY2020. Since the final year of this proposal was FY2020, the results for two fiscal years were summarized. The purpose of research was to improve the criticality safety analysis methods in the case of fuel debris removal with the collaboration with Russian university, which has a lot of experiences in the criticality analysis. This research has been performed as two fiscal years project in FY 2019 and FY 2020 by Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) and Tokyo City University (TCU) as the Japanese side, and National Research Nuclear University MEPhI as the Russian side.
Yanagisawa, Hiroshi
JAEA-Technology 2021-023, 190 Pages, 2021/11
Computational analyses on nuclear criticality characteristics were carried out for heterogeneous lattice systems composed of water moderator and fuel rods utilized in low-power research and test reactors, in which the depletion of fuel due to burnup is relatively small, by using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP Version 2 with the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-4.0. In the analyses, the minimum critical number of fuel rods was evaluated using calculated neutron multiplication factors for the heterogeneous systems of the uranium dioxide fuel rod in the Static Experiments Critical Facility (STACY) and the Tank-type Critical Assembly (TCA), and the uranium-zirconium hydride fuel rod in the Nuclear Safety Research Reactor (NSRR). In addition, six sorts of the ratio of reaction rates, which are components of neutron multiplication factors, were calculated in the analyses to explain the variation of neutron multiplication factors with the ratio of water moderator to fuel volume in a unit fuel rod cell. Those results of analyses are considered to be useful for the confirmation of reasonableness and validity of criticality safety measures as data showing criticality characteristics for water-moderated heterogeneous lattice systems composed of the existing fuel rods in research and test reactors, of which criticality data are not sufficiently provided by the Criticality Safety Handbook.
Sahboun, N. F.; Matsumoto, Toshinori; Iwasawa, Yuzuru; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2021 (ASRAM 2021) (Internet), 15 Pages, 2021/10
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2020-041, 30 Pages, 2020/12
JAEA/CLADS had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project in FY2019. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Improvement of Critical Safety Technology in Fuel Debris Retrieval" conducted in FY2019.
Yamane, Yuichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(8), p.926 - 931, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)An equation of power in subcritical quasi-steady state has been derived based on one-point kinetics equations for the purpose of utilizing it for the development of timely reactivity estimation from complicated time profile of neutron count rate. It linearly relates power,  , to a new variable
, to a new variable  , which is a function of time differential of the power. It has been confirmed by using one-point kinetics code, AGNES, that the calculated points (
, which is a function of time differential of the power. It has been confirmed by using one-point kinetics code, AGNES, that the calculated points (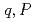 ) are perfectly in a line described by the new equation and that points (
) are perfectly in a line described by the new equation and that points (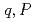 ) calculated from transient subcritical experiments by using TRACY made a line with a slope indicated by the new equation.
) calculated from transient subcritical experiments by using TRACY made a line with a slope indicated by the new equation.
Task Force on Writing Textbook of Nuclear Fuel Materials
JAEA-Review 2020-007, 165 Pages, 2020/07
The present textbook was written by Task Force on Writing Textbook of Nuclear Fuel Materials at the Nuclear Science Research Institute in order to improve technological abilities of engineers and researchers who handle nuclear fuel materials. The taskforce consists of young and middle class engineers each having certification for chief engineer of nuclear fuel. The present textbook mainly deals with uranium and plutonium, and shows their nuclear properties, physical and chemical properties, and radiation effects on materials and human body. It also presents basic matters for safety handling of nuclear fuel materials, such as handling of nuclear fuel materials with hood and glovebox, important points in storage and transportation of nuclear fuel materials, radioactive waste management, radiation safety management, and emergency management. Furthermore, incident cases at domestic and foreign nuclear fuel materials facilities are compiled to learn from the past.
Ueta, Shohei; Mizuta, Naoki; Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Tachibana, Yukio; Honda, Masaki*; Saiki, Yohei*; Takahashi, Masashi*; Ohira, Koichi*; Nakano, Masaaki*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 357, p.110419_1 - 110419_10, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)The concept of a plutonium (Pu) burner HTGR is proposed to incarnate highly-effective Pu utilization by its inherent safety features. The security and safety fuel (3S-TRISO fuel) employs the coated fuel particle with a fuel kernel made of plutonium dioxide (PuO ) and yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) as an inert matrix. This paper presents feasibility study of Pu burner HTGR and R&D on the 3S-TRISO fuel.
) and yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) as an inert matrix. This paper presents feasibility study of Pu burner HTGR and R&D on the 3S-TRISO fuel.
Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Nagatake, Taku; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Tojo, Masayuki*; Goto, Daisuke*; Nishimura, Satoshi*; Suzuki, Hiroaki*; Yamato, Masaaki*; Watanabe, Satoshi*
Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-27) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2019/05
In this research program, cladding oxidation model in SFP accident condition, and numerical simulation method to evaluate capability of spray cooling system which was deployed for spent fuel cooling during SFP accident, have been developed. These were introduced into the severe accident codes such as MAAP and SAMPSON, and SFP accident analyses were conducted. Analyses using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) code were conducted as well for the comparison with SA code analyses and investigation of detail in the SFP accident. In addition, three-dimensional criticality analysis method was developed as well, and safer loading pattern of spent fuels in pool was investigated.
Nuclear Safety Research Center, Sector of Nuclear Safety Research and Emergency Preparedness
JAEA-Review 2018-022, 201 Pages, 2019/01
Nuclear Safety Research Center (NSRC), Sector of Nuclear Safety Research and Emergency Preparedness, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is conducting technical support to nuclear safety regulation and safety research based on the Mid-Long Term Target determined by Japanese government. This report summarizes the research structure of NSRC and the cooperative research activities with domestic and international organizations as well as the nuclear safety research activities and results in the period from JFY 2015 to 2017 on the nine research fields in NSRC; (1) severe accident analysis, (2) radiation risk analysis, (3) safety of nuclear fuels in light water reactors (LWRs), (4) thermohydraulic behavior under severe accident in LWRs, (5) materials degradation and structural integrity, (6) safety of nuclear fuel cycle facilities, (7) safety management on criticality, (8) safety of radioactive waste management, and (9) nuclear safeguards.
Okuno, Hiroshi; Suyama, Kenya; Ryufuku, Susumu*
JAEA-Review 2017-010, 93 Pages, 2017/06
There is an ongoing discussion on the application of burnup credit to the criticality safety controls of facilities that treat spent fuels. With regard to such application of burnup credit in Japan, this document summarizes the current technical status of the prediction of the isotopic composition and criticality of spent fuels, as well as safety evaluation concerns and the current status of legal affairs. This report is an English translation of A Guide to Introducing Burnup Credit, Preliminary Version, originally published in Japanese as JAERI-Tech 2001-055 by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Facility Safety Research Committee.
Amano, Yuki; Watanabe, Koji; Masaki, Tomoo; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Abe, Hitoshi
JAEA-Technology 2016-012, 21 Pages, 2016/06
To contribute to safety evaluation of fire accident in fuel reprocessing plants, solvent extraction behavior of ruthenium, which could form volatile species, was investigated. Distribution ratios of ruthenium at fire accident conditions were obtained by extraction experiments with several solvent composition at different temperature as parameters. In order to investigate release behavior of ruthenium and europium at fire accident, release ratios of ruthenium and europium were also obtained by solvent combustion experiments.
 -radiation on a direct disposal system for spent nuclear fuel, 1 Review of research into the effects of
-radiation on a direct disposal system for spent nuclear fuel, 1 Review of research into the effects of  -radiation on the spent nuclear fuel, canisters and outside canisters
-radiation on the spent nuclear fuel, canisters and outside canistersKitamura, Akira; Takase, Hiroyasu*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(1), p.1 - 18, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:12.5(Nuclear Science & Technology)Not only geological disposal of vitrified waste generated by spent fuel (SF) reprocessing, but also the possibility of disposing of SF itself in deep geological strata (hereinafter "direct disposal of SF") may be considered in the Japanese geological disposal program. In the case of direct disposal of SF, the radioactivity of the waste is higher and the potential effects of the radiation are greater. Specific examples of the possible effects of radiation include: increased amounts of canister corrosion; generation of oxidizing chemical species in conjunction with radiation degradation of groundwater and accompanying oxidation of reducing groundwater; and increase in the dissolution rate and the solubility of SF. Focusing especially on the effects of  -radiation in safety assessment, this study has reviewed research into the effects of
-radiation in safety assessment, this study has reviewed research into the effects of  -radiation on the spent nuclear fuel, canisters and outside canisters.
-radiation on the spent nuclear fuel, canisters and outside canisters.
 -radiation on a direct disposal system for spent nuclear fuel, 2; Review of research into safety assessments of direct disposal of spent nuclear fuel in Europe and North America
-radiation on a direct disposal system for spent nuclear fuel, 2; Review of research into safety assessments of direct disposal of spent nuclear fuel in Europe and North AmericaKitamura, Akira; Takase, Hiroyasu*; Metcalfe, R.*; Penfold, J.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(1), p.19 - 33, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)Not only geological disposal of vitrified waste generated by spent fuel (SF) reprocessing, but also the possibility of disposing of SF itself in deep geological strata (hereinafter "direct disposal of SF") may be considered in the Japanese geological disposal program. In the case of direct disposal of SF, the radioactivity of the waste is higher and the potential effects of the radiation are greater. Specific examples of the possible effects of radiation include: increased amounts of canister corrosion; generation of oxidizing chemical species in conjunction with radiation degradation of groundwater and accompanying oxidation of reducing groundwater; and increase in the dissolution rate and the solubility of SF. Therefore, the influences of radiation, which are not expected to be significant in the case of geological disposal of vitrified waste, must be considered in safety assessments for direct disposal of SF. Focusing especially on the effects of  -radiation in safety assessment, this study has reviewed safety assessments in countries other than Japan that are planning direct disposal of SF. The review has identified issues relevant to safety assessment for the direct disposal of SF in Japan.
-radiation in safety assessment, this study has reviewed safety assessments in countries other than Japan that are planning direct disposal of SF. The review has identified issues relevant to safety assessment for the direct disposal of SF in Japan.
Goto, Minoru; Demachi, Kazuyuki*; Ueta, Shohei; Nakano, Masaaki*; Honda, Masaki*; Tachibana, Yukio; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Aihara, Jun; Fukaya, Yuji; Tsuji, Nobumasa*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st International Conference & Exhibition; Nuclear Fuel Cycle for a Low-Carbon Future (GLOBAL 2015) (USB Flash Drive), p.507 - 513, 2015/09
A concept of a plutonium burner HTGR named as Clean Burn, which has a high nuclear proliferation resistance, had been proposed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In addition to the high nuclear proliferation resistance, in order to enhance the safety, we propose to introduce PuO -YSZ TRISO fuel with ZrC coating to the Clean Burn. In this study, we conduct fabrication tests aiming to establish the basic technologies for fabrication of PuO
-YSZ TRISO fuel with ZrC coating to the Clean Burn. In this study, we conduct fabrication tests aiming to establish the basic technologies for fabrication of PuO -YSZ TRISO fuel with ZrC coating. Additionally, we conduct a quantitative evaluation of the security for the safety, a design of the fuel and the reactor core, and a safety evaluation for the Clean Burn to confirm the feasibility. This study is conducted by The University of Tokyo, Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Fuji Electric Co., Ltd., and Nuclear Fuel Industries, Ltd. It was started in FY2014 and will be completed in FY2017, and the first year of the implementation was on schedule.
-YSZ TRISO fuel with ZrC coating. Additionally, we conduct a quantitative evaluation of the security for the safety, a design of the fuel and the reactor core, and a safety evaluation for the Clean Burn to confirm the feasibility. This study is conducted by The University of Tokyo, Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Fuji Electric Co., Ltd., and Nuclear Fuel Industries, Ltd. It was started in FY2014 and will be completed in FY2017, and the first year of the implementation was on schedule.